– Ananaya Rana
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a significant health concern affecting young individuals, particularly adolescent girls and young women. This comprehensive review explores the etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and management strategies of PCOS in the context of youth health. Through an analysis of recent scientific literature and clinical guidelines, this article aims to enhance understanding of PCOS among healthcare professionals and young individuals affected by this condition.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in Youth Health
PCOS presents unique challenges to youth health, impacting physical, emotional, and reproductive well-being. Despite its prevalence, PCOS often goes undiagnosed in adolescents, leading to long-term health consequences. This review aims to shed light on the complexities of PCOS in youth, facilitating early detection and tailored management approaches.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
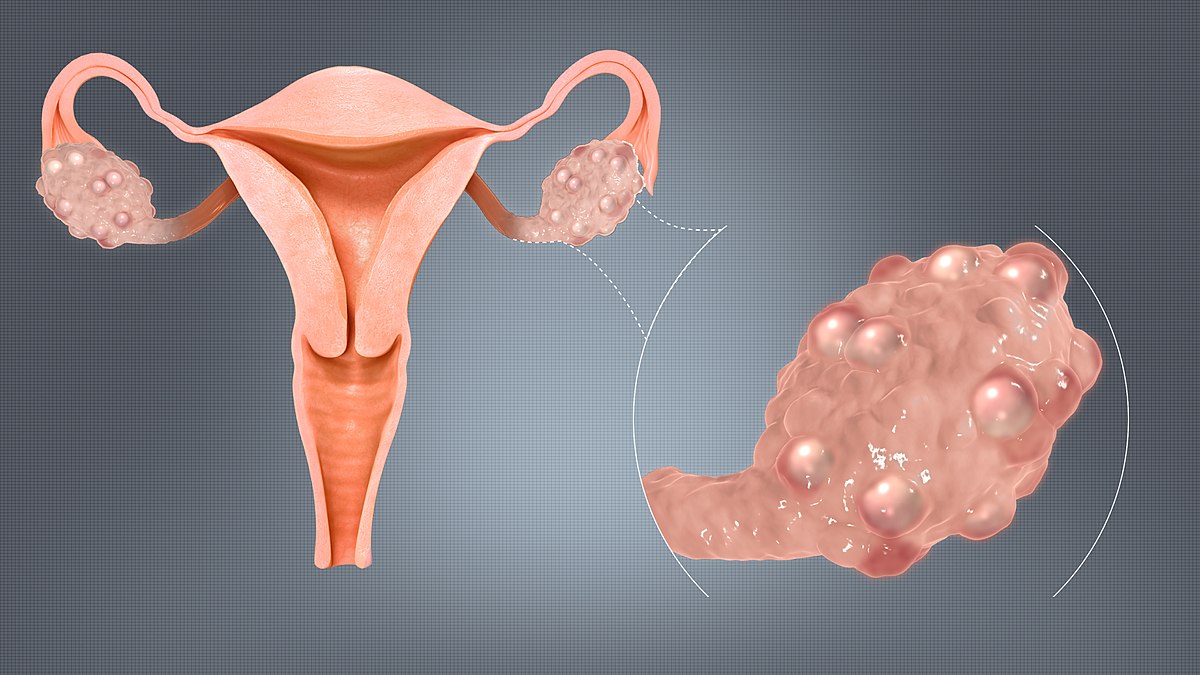
The etiology of PCOS in youth involves a complex interplay of genetic predispositions, hormonal fluctuations, and environmental factors. Hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and ovarian dysfunction contribute to the heterogeneous clinical manifestations observed in young individuals with PCOS. Genetic studies have identified several susceptibility loci associated with PCOS in adolescents, highlighting the genetic basis of this syndrome.
Clinical Manifestations
PCOS manifests differently in youth compared to adults, presenting with unique clinical features such as irregular menstrual cycles, acne, hirsutism, and obesity. Diagnostic criteria for PCOS in adolescents may differ from those in adults, necessitating careful consideration of age-specific manifestations. Timely recognition of PCOS in youth is crucial to mitigate long-term health risks and optimize reproductive outcomes.
Management Strategies
The management of PCOS in youth focuses on addressing hormonal imbalances, metabolic disturbances, and psychological well-being. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and regular physical activity, play a central role in managing PCOS symptoms and preventing complications such as insulin resistance and obesity. Pharmacological interventions, such as oral contraceptives and insulin-sensitizing agents, may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate hyperandrogenism in adolescents with PCOS.
Impact on Youth Health
PCOS significantly impacts the health and quality of life of young individuals, affecting physical, emotional, and social aspects of well-being. Adolescents with PCOS are at increased risk of developing obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, underscoring the importance of early intervention and comprehensive management strategies. Moreover, PCOS-related symptoms such as acne and hirsutism can have profound psychosocial implications, affecting self-esteem and interpersonal relationships in youth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCOS represents a critical health concern in youth, necessitating a holistic approach to diagnosis, management, and support. By understanding the unique challenges faced by young individuals with PCOS and implementing evidence-based interventions, healthcare professionals can improve outcomes and promote long-term health and well-being in this vulnerable population. Continued research efforts are needed to further elucidate the complexities of PCOS in youth and develop tailored approaches to address their specific needs.